Introduction
Hydroponic agriculture is a revolutionary farming method that differs from traditional soil-based farming.
Instead of relying on soil, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, allowing them to thrive in a controlled environment.
Hydroponic agriculture is a innovative technique provides sustainable and space-efficient way to grow food, making it especially valuable in urban areas and areas with poor soil quality.
With precise control over nutrients, water, and light, hydroponics not only increases crop yields but also reduces the need for pesticides and excessive water use.
As global food demand grows, hydroponic farming is a smart, efficient way to grow crops in the future of agriculture.
Buy Hydroponic kit for In dore home
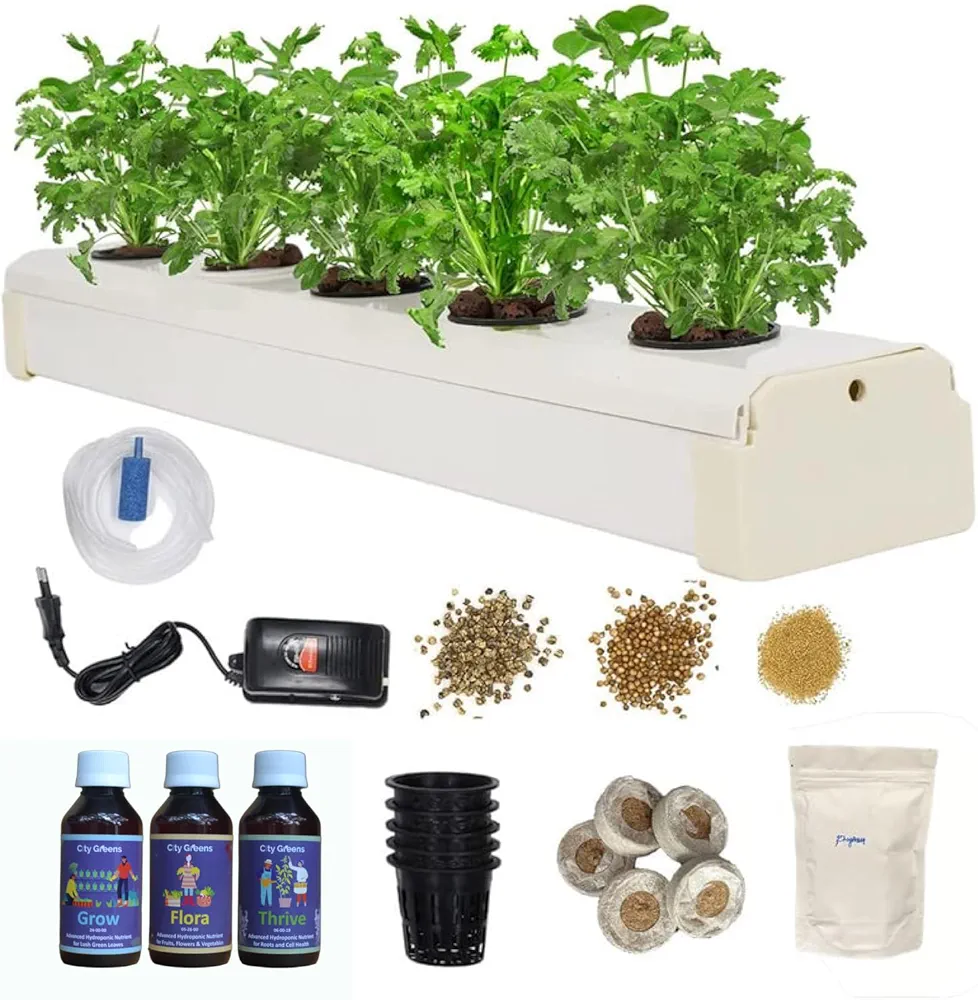

Table of Contents
Types of Hydroponic Systems
1.Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)

In hydroponic agriculture Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is one of the most efficient and popular hydroponic systems used to grow a variety of crops without soil.
In this method, a thin stream or “film” of nutrient-rich water is continuously passed over the roots of plants, which are placed in a slightly inclined tube or hose.
This constant flow ensures that the roots receive the right balance of nutrients, oxygen, and water, promoting faster and healthier growth.
One of the main advantages of NFT is that it consumes less water and nutrients, making it a sustainable option for modern agriculture.
It is particularly suitable for light, fast-growing crops such as leafy greens, herbs and strawberries.
Since the roots are exposed to air in this system, they are well oxygenated, which further promotes plant growth.
With proper setup and monitoring, nutrient film technology provides a high-yield, space-saving solution that is ideal for urban farms, greenhouses, and commercial hydroponic ventures.
NFT is more than a technology – it’s a smart step toward the future of sustainable farming.
2.Deep Water Culture (DWC)

In hydroponic agriculture Deep water culture (DWC) is a popular hydroponic Agriculture in which plant roots are suspended in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water.
Unlike other methods, DWC completely immerses the roots in water, allowing them to continuously absorb nutrients and oxygen.This constant access to essential elements promotes faster growth and healthier plants.
This system usually consists of a container filled with nutrient solution, mesh pots to hold the plants, and an air pump with air stones to oxygenate the water. The air bubbles play an important role in preventing root rot and keeping the plants from drowning.
DWC is especially preferred by beginners because of its simple installation, affordability, and low maintenance.
It is ideal for growing lettuce, herbs, and other leafy greens, although it can also support fruit-bearing plants with the proper adjustments.
One of the main advantages of DWC is that it promotes faster plant growth since it absorbs nutrients directly.
However, it is important to maintain water temperature and pH levels to avoid nutrient imbalances and disease.
With its ease of use and high efficiency, deep water culture is an excellent way to enter the world of hydroponics and a smart solution for anyone looking to grow fresh food with minimal space and resources.
3.Drip System

The drip system is one of the most versatile and widely used methods in hydroponic farming.
It works by delivering nutrient-rich water directly to the base of each plant through a network of tubes, emitters, or drip lines.
This method ensures that plants receive a constant and controlled supply of nutrients and moisture, minimizing water wastage and maximizing growth potential.
One of the main advantages of a drip system is its adaptability. It can be adapted to small-scale setups like indoor gardens and large commercial greenhouses.
Growers can automate the system with timers and sensors, allowing precise control over irrigation schedules and nutrient delivery.
This not only saves labor but also reduces the likelihood of overwatering or nutrient loss.Unlike traditional soil cultivation, the drip system keeps the root zone optimally moist without waterlogging, promoting better oxygen availability to the roots. As a result, plants grow faster, yield more, and are less affected by diseases.
Overall, drip systems offer a smart, sustainable solution for modern agriculture – combining resource efficiency with high productivity.
4.Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
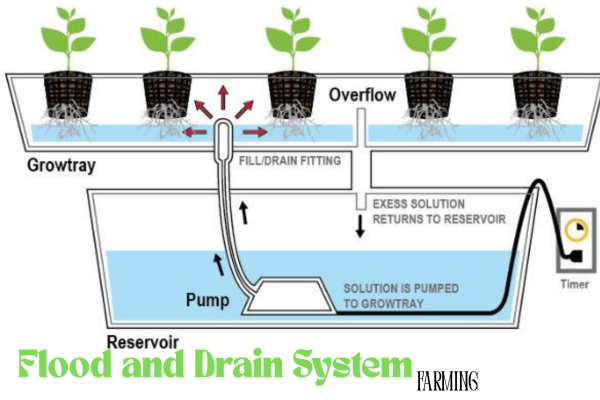
The ebb and flow system, also known as flood and drain, is a dynamic and efficient hydroponic Agriculture used to grow a wide variety of plants.
It works by temporarily filling the grow tray with nutrient solution and then draining it back into the reservoir for hydroponic farming.
This cycle is repeated at regular intervals using a pump connected to a timer.
During the flooding phase, the plant’s roots absorb water, oxygen, and essential nutrients.
Once the solution is drained, the roots are exposed to air, which improves oxygenation and promotes healthy growth.
This balance of moisture and air prevents root rot and promotes strong root growth.This system is relatively simple to build and maintain, making it ideal for hobbyists as well as commercial growers.
It can accommodate a variety of growing mediums such as clay pebbles, perlite or rockwool, Which helps to keep the plants stable and maintain moisture between cycles.
A major advantage of the ebb and flow system is its cost-effectiveness and scalability.
Whether for a small indoor garden or a large-scale setup, this method provides a reliable way to grow high-yielding crops with minimal water wastage.
In short, the Ebb and Flow system is a combination of simplicity, flexibility and efficiency, making it a powerful tool in modern hydroponic Agriculture.
5.Aeroponics
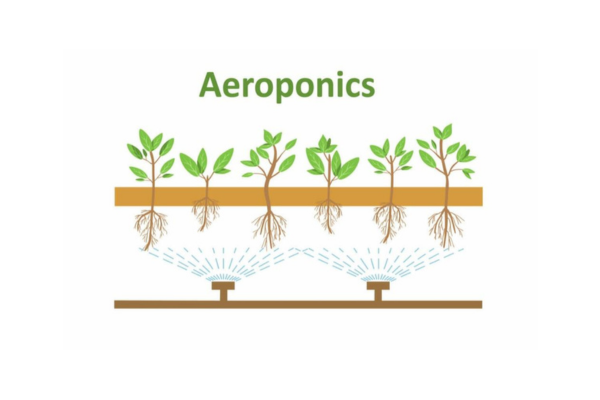

Aeroponics is a cutting-edge hydroponic Farming in which plants are grown in the air without any soil or growing medium.
In this system, the roots are suspended in a closed or semi-closed environment and are regularly sprayed with a nutrient-rich water solution.The most notable benefit of aeroponics is its efficiency.
Since the roots are exposed to more oxygen, plants grow faster and absorb nutrients more effectively.Additionally, water use is significantly reduced – making this one of the most sustainable farming methods available.
This technique is ideal for urban farming, vertical gardens, and environments with limited space.
It is also being used in research to grow food in space due to its minimal resource requirements.
In conclusion, aeroponics offers a high-tech, eco-friendly solution to modern agricultural challenges, paving the way for healthier crops and a greener planet in hydroponic Agriculture.
6.Wick System
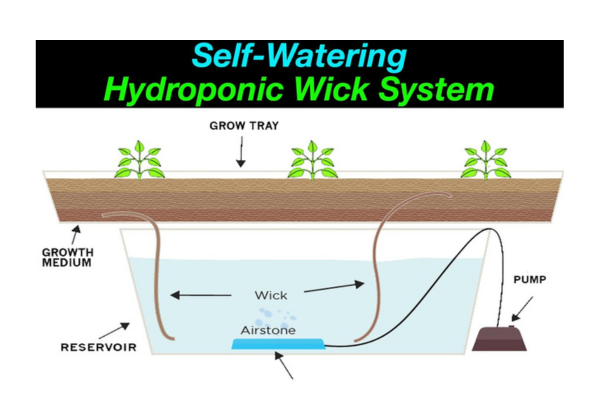
The wick system is one of the simplest and most beginner-friendly methods of hydroponic Agriculture.
It operates without any pumps or moving parts, making it a passive system that is easy to set up and maintain.In this system, a wick (usually made of cotton, nylon or other absorbent material) connects the plant’s root zone to a reservoir filled with a nutrient solution.
The wick draws the solution up through capillary action, slowly delivering water and nutrients to the plant’s roots.
While the wick system is ideal for small plants and herbs such as lettuce, basil or spinach, it is not suitable for larger, water-hungry crops due to the limited nutrient delivery rate.
Its biggest advantage is that it is low cost and low maintenance. It does not require electricity, making it perfect for off-grid farming or education.
Overall, the wick system is a great entry point for those new to hydroponics, providing a simple and effective way to grow plants without soil
Benefits of Hydroponic Agriculture
Saves up to 90% more water than traditional farming.
- Faster plant growth and higher yields.
- Space-saving, ideal for urban farming.
- No soil-borne diseases or weeds.
- Precise control over nutrients and growing conditions.
Common Crops Grown Hydroponic Agriculture
- Lettuce, spinach, kale.
- Tomatoes, cucumbers.
- Herbs like basil, mint, and cilantro.
- Strawberries and peppers.
Hydroponics Agriculture vs Traditional Farming
As the demand for sustainable and efficient farming methods grows, comparisons between hydroponics agriculture and traditional farming are becoming very important.
Both methods aim to produce healthy crops, but they differ greatly in technique, resource use, and environmental impact.
Hydroponic Agriculture is a soilless farming technique in which plants grow in a nutrient-rich water solution.
This allows precise control over nutrients, water, and environmental conditions.
This method uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming and can be cultivated year-round, even in confined or urban areas.
It also reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, leading to cleaner and faster-growing crops.
Traditional farming, on the other hand, relies on the soil and natural weather conditions.
Although it promotes a wide variety of crops and has been practiced for centuries, it is often criticized for causing soil erosion,Pest attacks, unpredictable weather and excessive use of water.
Key differences
- Water Use: Water use is far more efficient in hydroponic Agriculture.
- Space Requirements: Hydroponics can be done vertically and in smaller areas.
- Yield: The controlled environment in hydroponics often yields higher yields.
- Maintenance: Traditional farming relies on labor and weather,while hydroponics needs technical setup and monitoring.
Initial Setup Requirements
Starting a hydroponic farming system requires thoughtful planning and the right equipment to ensure successful plant growth.
Unlike traditional agriculture, hydroponics focuses on precision, resource control, and a clean growing environment.
Here are the key initial setup requirements:
Growing Space:
Choose a suitable area with access to electricity and controlled lighting – indoor or outdoor. Greenhouses, balconies and spare rooms are commonly used.
Type of Hydroponic System:
Decide on the type of system you want to install, such as NFT (nutrient film technique), DWC (deep water culture), drip system or wick system. Each has different needs in terms of space, water flow and equipment.
Water Reservoir:
A container to hold the nutrient solution is essential. It must be large enough to supply water to all the plants and must be easy to clean and refill.
Grow Trays or Channels:
These hold the plants and direct the nutrient solution. Materials such as food-grade plastic or PVC pipe are commonly used.
Growing Medium:
Since there is no soil, you will need an inert medium like cocopeat, perlite, vermiculite or clay pellets to support the plant roots.
Nutrient solution:
Plants require a balanced mix of essential nutrients. Buy or prepare a hydroponic nutrient solution suitable for your crop.
Water pump and air pump (if needed):
For systems like DWC or NFT, pumps help circulate water and maintain oxygen levels in the roots.
pH and EC Meters:
Monitoring pH and electrical conductivity ensures the nutrient solution remains optimal for plant health.
Lighting (for indoor setup):
If natural sunlight is not available, LED grow lights or fluorescent lights are required to provide adequate lighting.
Plant Containers or Net Pots:
These hold individual plants and are placed inside a grow tray or pipe.
Challenges in Hydroponic Farming
Hydroponic Agriculture offers many benefits, but it also comes with several challenges.
The biggest problem is the initial cost of setup, which can be high due to the need for specialized equipment and infrastructure.
Additionally, growers must have a good understanding of nutrient management and water chemistry – imbalances can quickly harm plants.
Technical failures such as a pump failure or power outage can disrupt the entire system and affect the health of the crop.
Hydroponic agriculture also requires constant monitoring and maintenance, which requires time and attention from the grower.
Finally, not all crops are suitable for hydroponics, and disease or algae growth in water systems can pose risks if not properly controlled.
Despite these challenges, with proper planning and knowledge, hydroponic agriculture can be a sustainable and profitable venture.
Is Hydroponic Agriculture Profitable?
Yes, hydroponic agriculture can be highly profitable, especially when managed efficiently and grown at the proper scale.
By growing plants in a controlled, soilless environment, farmers can achieve faster growth rates, higher yields and year-round production, thereby increasing income opportunities.
The biggest advantage is space and resource efficiency. Hydroponic agriculture systems use up to 90% less water and can be set up in urban areas, rooftops or unused indoor spaces – reducing land dependency and transportation costs.
High-demand crops such as lettuce, herbs, strawberries and exotic vegetables often sell at higher prices to local markets, restaurants and the health-conscious consumer segment.
However, profitability depends on several factors:Initial investment in equipment and setup Market access and pricing Energy and nutrient costs, Technical knowledge and system management.With proper planning, crop selection and marketing, hydroponics offers a sustainable and scalable business model that can yield strong profits in both small-scale and commercial agricultural ventures.
Future of Hydroponic Agriculture
The future of hydroponic agriculture looks promising as the world moves towards sustainable and efficient food production.
With increasing urbanisation, decreasing arable land and water scarcity, hydroponics offers a smart solution by using less space, minimal water and no soil.
Advances in technology – such as automation, AI monitoring and vertical farming – are making hydroponics more accessible and productive.
It also supports year-round farming and can thrive in urban environments, deserts or even space missions.
As consumer demand for fresh, pesticide-free produce grows, hydroponic farming is set to play a major role in reshaping modern agriculture and ensuring food security for future generations.
Government Support and Training in India (if local context is needed)
In India, the government is increasingly recognising the potential of hydroponic farming as a sustainable solution for food production.
Through various schemes under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, polyhouse, greenhouses, and protected cultivation systems that support hydroponics.
Organisations like National Horticulture Board (NHB) and National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) provide financial assistance and loans at low interest rates to promote modern agricultural techniques.
Training programmes are also organised by Krishi Vigyan Kendra’s (KVK’ s), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) institutes and private Agri- tech companies to educate farmers and entrepreneurs on hydroponic systems, nutrient management and system maintenance.
This growing support is empowering a new generation of agricultural entrepreneurs and helping India move towards smart, climate-friendly farming.
Conclusion
Hydroponic farming is a revolutionary step in sustainable agriculture.
By eliminating the need for soil and optimising the use of water and nutrients, it provides a clean, efficient and high-yielding way to grow crops.
Ideal for urban areas and resource-limited regions, hydroponics can help ensure food security while reducing the environmental impact of traditional farming.
With increasing government support, technological advancements and growing market demand for fresh, chemical-free produce, hydroponic farming has immense potential for the future of agriculture.
Also some profitable Agriculture business is mentioned below:


7 thoughts on “Hydroponic Agriculture”